Address: Sambhav Clinic, K-30 Pallavpuram, Meerut, Phase 2, Uttar pradesh (India)
Call For Appointment : +91 7037709494 +91 9627539595

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
What Is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
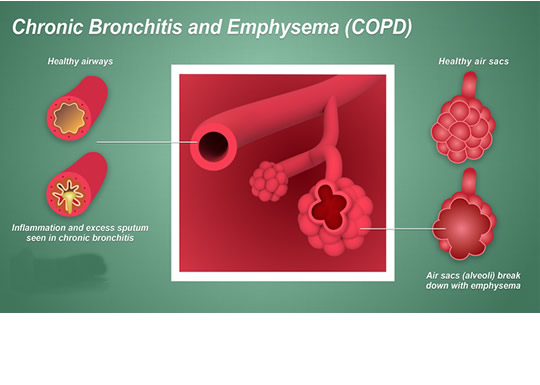
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a kind of chronic inflammatory disease of lungs that leads to obstruction of airflow from the lungs. There are two primary forms of COPD, i.e., chronic bronchitis (characterized by long term cough along with mucus discharge and inflammation in the lining of bronchial tubes) and emphysema (characterized by damaging of the lungs and alveoli at the end of bronchioles over a certain period).
COPD is a treatable condition; proper management and medication are necessary. Most people with COPD can get decent symptom control and risk of other associated disorders by improving their quality of life.
Effects of COPD on Health and Life
Lifelong management against symptoms is required once COPD is diagnosed. The patient has to follow the advice of his healthcare practitioner and must maintain a healthy lifestyle at any cost.
COPD can be used as an essential factor in determining a person’s health status, but its effects are known to be more resilient on the physical and mental aspects of health. People with severe COPD have rated their physical health to be very low. According to them, they now walk slow and can merely cover a short distance without getting tired or fatigued. People with COPD often complain about pain, low sleep quality, sedentary behavior, and less body strength.
Patients with this disorder are considered to have a compromised disease-specific mental health status and often experience cognitive status, anxiety, depression, and feeling of sadness. Usually, people with COPD are less involved in social gatherings and their marital status, social network size; loneliness and unemployment cause them to lead an unpleasant life.
Symptoms of COPD
The initial symptoms may be mild. Once the disease starts to progress, symptoms can become more severe and consistent, making it very difficult to breathe. The patients may go through the tightness in the chest area, more production of mucus/sputum and wheezing.
The first mild and quiet symptoms of COPD are:
- The occasional difficulty in breathing (after exercise)
- Recurrent coughing (mild to moderate)
- The need for clearing throat repeatedly
These changes are often confused with the symptoms of common cold and flu, but making subtle changes in routine (low physical activity) can improve the condition.
When the disease spreads, symptoms can become severe and hard to ignore. The advanced symptoms of COPD are:
- Shortness of breath even after a mild physical activity
- Wheezing (high pitch breathing with noise)
- Tightness in chest
- Chronic cough with sputum
- Frequent cold, flu attacks, and respiratory tract infections
- Tiredness, fatigue, and weakness
COPD (Late Stage) the patient may also go through:
- Swelling of body parts such as feet, legs, and ankles
- Weight loss
- Lethargy
- Blue/gray fingernails and lips
Stages of COPD
There are four stages of COPD:
- Stage I (Mild)
In this stage, the flow of air is somewhat limited, but people fail to notice it much. The patient may cough and spit out mucus every once in a while.
- Stage II (Moderate)
When this stage is reached, the airflow to the lungs starts to become worse. The patient is often breathless or experiences difficulty in breathing even after being physically inactive. It is the stage where the symptoms are most prominent, and people start getting help from their doctors.
- Stage III (Severe)
The flow of air towards the lungs and difficulty in breathing aggravates even more. A person is unable to perform routine tasks or any daily exercise. The symptoms flare up occasionally, which is also termed as an exacerbation.
- Stage IV (Very severe)
The patient may experience heart or lung failure. The airflow to lungs is entirely restricted due to which it becomes tough to catch breath even in resting position.
Diagnosis of COPD
There are no tests to determine COPD, and diagnosis is made only based on symptoms and their severity. When you consult your healthcare provider, make sure you provide them with all the related information such as
- Smoking
- Exposure to any lung irritants
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Family history or genetics of COPD
- Asthma or other respiratory tract disorder
- Any OTC medicine under constant use
Based on the provided information, the doctor may ask to do these tests:
- Spirometry
This non-invasive test is performed to analyze your lung function. The patient has to breathe deep and blow in the tube.
- X-Ray or CT scan
These imaging tests are performed to have a detailed look at the lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
- Arterial Blood Gas Test
This blood test is only done to determine how well your lungs are capable of bringing oxygen in the blood vessels and in removing carbon dioxide along with other waste from the body.
Prevention from COPD
To prevent the development of COPD. The following steps should be taken:
- No Smoking
If you smoke regularly, be sure to quit it in time. You can ask your doctor to give you recommendations about the right products and services for assistance.
Also, avoid chemical fumes and secondhand smoke as much as possible.
- Avoid Tobacco Exposure
Both active and passive measures should be taken to limit exposure to tobacco. People who smoke and use tobacco should be given interventions that target smoking cessation through pharmacotherapy and psychanalysis. In the beginning, minor short-term side effects may be seen, but with time, things can get settled giving life-long benefits.
- Vaccinations
Vaccinations fall under the category of secondary COPD prevention. People are advised to get regular vaccination shots against pneumonia and influenza.
- Healthy Eating
A healthy diet is essential to maintain inner strength and power. Try to take nutrient-rich diet through vegetables, fruits, and meat, but if they already are a part of your diet and you are still underweight, then it is recommended to consult your doctor for nutritional supplements and multivitamins.
- Regular Exercise
If a person experiences breathing difficulty, it may seem very hard to be physically active. However, regular exercise, even for 30 minutes, can improve your overall endurance, strength, and respiratory organs.
Copyright © 2021. All right reserved. Sambhav Clinic

